Ready to master your way to CAT exam success? At Quantifiers, we’ll make the world of averages not only understandable but also as easy as pie! Join us on this journey of mastering the Average concept with a sprinkle of wit and a dash of fun. This section will explore the idea of Average, how important it is to the CAT exam’s Quantitative Aptitude section, and how you can succeed with our experienced assistance.
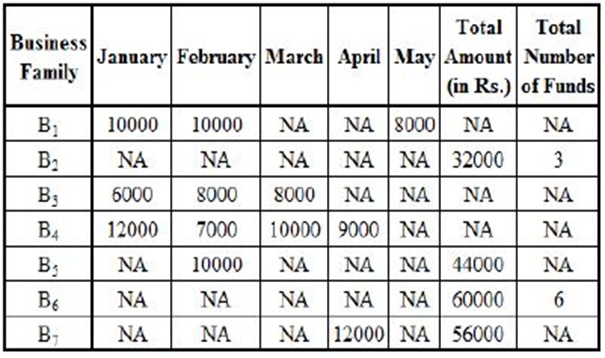
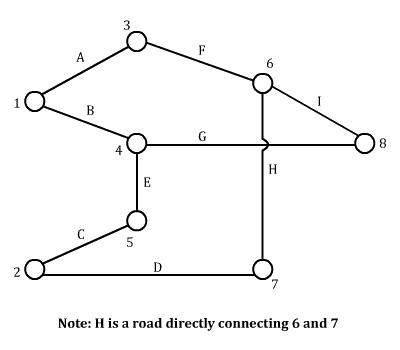
In our commitment to CAT exam excellence, Quantifiers presents a comprehensive collection of practice questions and thorough video explanations covering a wide array of DILR topics. While excluding specific categories, this section encompasses an assortment of challenging problems to refine your problem-solving skills and enhance your overall DILR proficiency.
Quantifiers’ DILR Miscellaneous section is designed to augment your CAT exam preparation by providing ample practice material and insightful explanations. Strengthen your foundation, refine your strategies, and excel in the DILR section with our comprehensive question bank and video explanations.